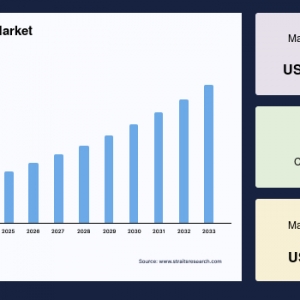
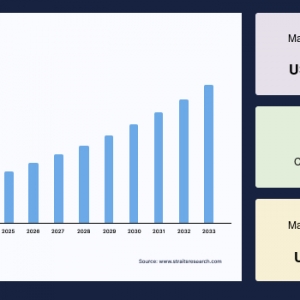
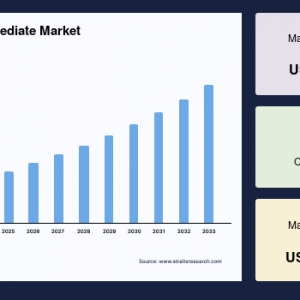
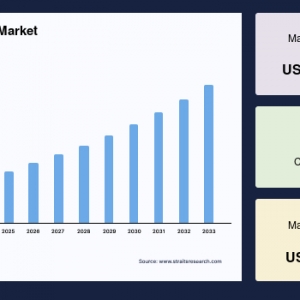
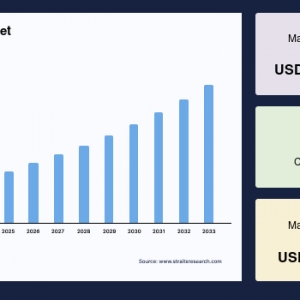
The global Railway Coupler Market was valued at USD 4.35 billion in 2024. It is expected to reach from USD 4.51 billion in 2025 to USD 6.06 billion in 2033, growing at a CAGR of 3.76% over the forecast period (2025-33).
Understanding Railway Couplers
A railway coupler is a mechanical device used to connect rolling stock in trains, enabling the transfer of traction and braking forces between cars. There are two main types of railway couplers: semi-permanent couplers and automatic couplers. Semi-permanent couplers provide a more permanent mechanical and pneumatic connection often used in passenger trains, while automatic couplers allow for quicker and safer coupling especially useful for freight and high-speed trains. The choice of coupler has a significant impact on train safety, operational efficiency, and maintenance speed.
Market Drivers and Trends
The primary market driver is the increasing dependence on rail freight transportation, which is bolstered by industrial growth and international trade. Companies in several countries rely heavily on importing raw materials, enhancing the demand for reliable freight train couplers. Additionally, infrastructural projects globally, including new rail lines and upgrades of existing rail networks, support the expansion of the railway coupler market. For example, India is expanding its railway system with new lines and doubling existing tracks, while China pursues extensive railway projects connecting Asia and Europe.
Technological innovation also plays a pivotal role. The concept of virtual coupling—where trains run closely together using advanced coupling technology to maximize track usage—holds promise to boost efficiency in both freight and passenger services. While still in development, virtual coupling can reduce travel times and operational costs by allowing multiple trains to operate closer without increasing collision risks.
Regional Market Insights
Asia Pacific dominates the railway coupler market thanks to large-scale rail projects and vast passenger and freight volumes. Indian Railways alone operates thousands of passenger and freight trains daily over an extensive network, and government-led initiatives to modernize and expand rail infrastructure are significant growth catalysts.
North America holds a substantial market share with the U.S. and Canada investing heavily in the expansion and modernization of rail freight networks. The U.S. plans to build an extensive national high-speed rail system by 2030, boosting demand for advanced couplers. Europe is also a critical market, driven by the popularity of high-speed trains and ongoing upgrades to coupler technology to improve safety and interoperability across countries, particularly as part of sustainability and green mobility initiatives.
The Middle East and Africa are showing steady growth despite delays in some railway projects. Large-scale projects like the GCC railway network and high-speed rail initiatives in Saudi Arabia are expected to drive demand once operational.
Market Segmentation
The railway coupler market segments itself by type, application, and sales channel. Semi-permanent couplers remain widely used in passenger trains due to their reliability for bogie connections. In contrast, automatic couplers are gaining traction in freight and high-speed trains for their operational efficiencies and safety improvements.
In terms of application, the market includes regular passenger trains, high-speed trains, and freight trains. High-speed train couplers are designed for safety and smooth rides due to higher speeds and more stringent operational requirements. Freight train couplers focus more on load-handling capacity, although they tend to have less demand compared to passenger train couplers due to safety and comfort being lesser priorities.
Sales channels include direct sales to large rail operators and distribution channels that involve retailers and wholesalers facilitating wider market penetration.
Challenges and Future Outlook
One of the key challenges in the railway coupler market is delay in railway projects due to financial and logistical issues, which can slow market growth. Compatibility and retrofitting older rail fleets with modern couplers also pose challenges because of design differences and high upgrade costs.
Despite these challenges, innovation toward smart couplers equipped with sensors for real-time diagnostics and predictive maintenance is expected to accelerate. The integration of AI and digital technology will further enhance operational safety and efficiency. Governments’ focus on expanding rail connectivity, green transportation, and automation in rail systems will continue to drive the demand for advanced railway coupler solutions.
In conclusion, the railway coupler market is poised for steady growth fueled by global infrastructural investments, rising rail freight demand, and technological advancements toward smarter, safer, and more efficient coupling systems. Asia Pacific leads in market volume, while North America and Europe show significant contributions from modernization and high-speed rail projects, reflecting a global trend toward enhanced rail connectivity and operational excellence.